A Complete Guide to Power Grid's 'Big Three'
As the energy transition accelerates, integrating large-scale renewable energy sources like solar and wind offers hope for sustainability. However, their inherent intermittency and volatility pose significant challenges to power grid stability.
1. Definitions
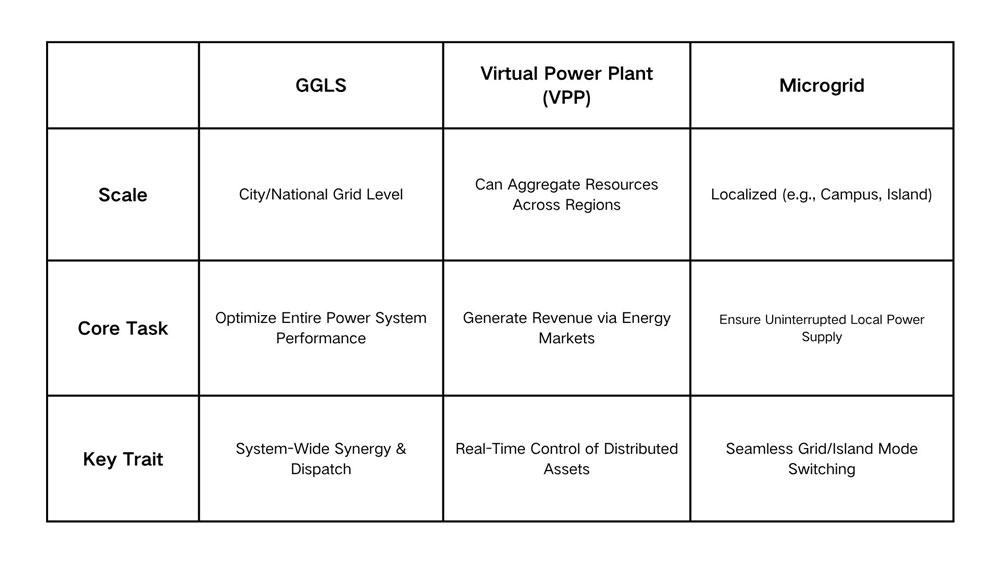
Generation-Grid-Load-Storage (GGLS): The Grid's "Master Conductor"
Aims to enhance renewable energy integration and ensure sustainable energy supply by holistically coordinating power generation sources, the grid network, electricity load (demand), and energy storage systems.

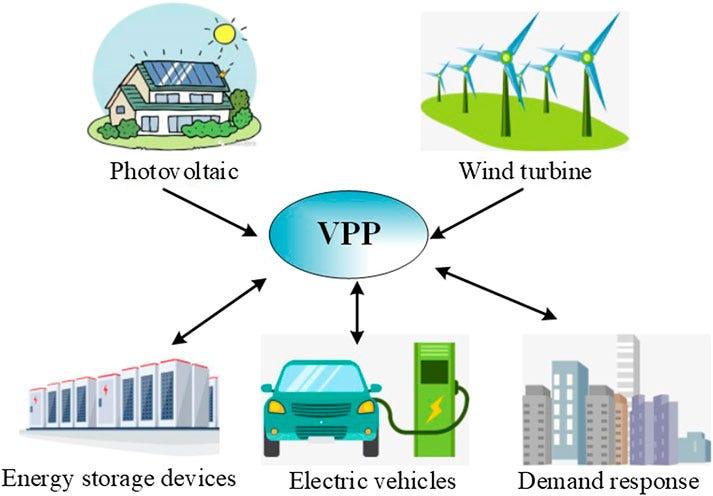
Virtual Power Plant (VPP): The Agile Market Player
Aggregates distributed energy resources (like rooftop solar and batteries) to provide flexible capacity, balance supply and demand, and actively participate in electricity markets.
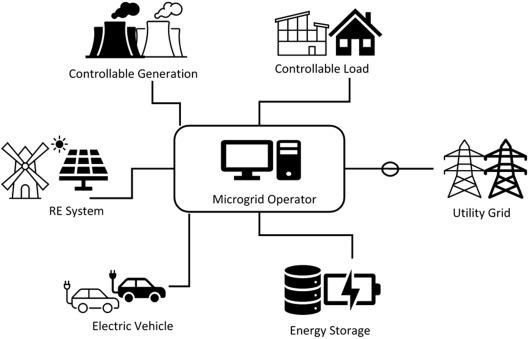
Microgrid: The Self-Sufficient "Local Community"
Leverages local renewable energy sources to generate and consume power within a defined area (e.g., campus, island), enabling localized energy transition and resilience.
2. Key Differences
3. Synergy in Action
In real-world applications, these technologies work together:
Microgrids ensure local power supply reliability.
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) aggregate resources within microgrids (like solar PV and batteries) to participate in broader energy markets.
The GGLS framework orchestrates the interaction between the main regional grid, VPPs, and microgrids, enabling seamless collaboration between large-scale and local power systems.
Ultimately, all three serve the energy transition. They enhance grid flexibility, reliability, and sustainability, boost renewable energy integration, strengthen grid resilience, optimize power resource allocation, and improve energy efficiency. Together, they provide crucial technical support for achieving carbon peaking and neutrality goals.

4. Conclusion
The traditional power grid is getting a major upgrade! GGLS, VPPs, and Microgrids are fundamentally reshaping the future energy landscape. Understanding these key technologies is essential as they transform the way we generate, manage, and consume electricity.